Analysis
The structure of the financial market and its functions
Quis autem vel eum iure reprehenderit qui in ea voluptate velit esse quam nihil molestiae consequatur, vel illum qui dolorem.

What is the world financial market and what is its architecture? What are financial market participants, their interaction, and their functions in the system? Economic indicators of financial markets.
Why do we need to study theory? The term “financial market” cannot be called a necessary one, a novice trader should learn first of all. Nevertheless, it is necessary to understand the structure of the financial market. The knowledge of how the financial market is arranged and how its participants interact with each other can suggest traders new investment opportunities, help reduce costs, and minimize risks. Without knowing the theory, it is impossible to become a professional practical trader. Spend 10 minutes of your time on this review. I hope that it will be useful and helpful for you!
When reading about financial markets and how you can earn money from them, do you know what you are dealing with? Banks, insurance funds, pension funds – the list of structures that make up the financial market is long enough. The article will provide a better understanding of how the financial market is structured and operates.
- 1. Trader’s keystones or all in due time
- 2. The structure of the financial market
- 3. Functions of the financial market
- 4. Participants in the financial market
- 5. Important indicators of the financial market – a note for trader
Trader’s keystones or all in due time
If someone tells you that understanding the “financial market” term, its structure, and its functions are essential to every trader, don’t believe them. That’s not right. However, we cannot say that this information is unnecessary. In the beginning, we don’t study an A to Z of Forex. We endeavor to acquire the necessary skills independently. Only when we’ve accumulated some experience by trial and error, do we turn ourselves to general knowledge. It may be a webinar, a trading course, educational articles, or A to Z books about Forex. According to the level of our expertise, we choose this or that kind of information. If a novice benefits from reading about 2 types of market analysis – fundamental and technical, – a more experienced trader will be interested in learning about the underpinnings of the underpinnings, that huge thing the currency market – his/her workplace- is a part of. As they say, all in due time.
The structure of the financial market
All the national and international markets make up the financial market. It incorporates banks, pension/insurance/currency funds, and many other economic institutions that help accumulate and redistribute money.
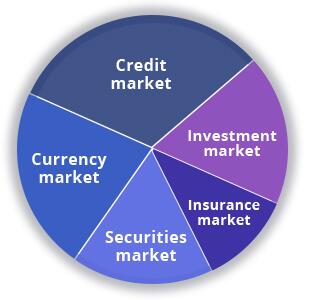
Being a complex system, the financial market has a multilevel structure including 5 market segments:
1. Foreign exchange market (Forex) or Currency market
It is the market in which the subject of its participant’s interaction is the currency and everything related to its equivalent. Derivative instruments may also serve as trading instruments (for example, currency CFDs). Depending on the form, the settlement can be cash or non-cash; according to the transaction term, the market can be current (spot) and derivatives currency markets. Derivatives market contracts can be:
- 1. Forward contracts. A forward contract is customized between two parties at an agreed price; the intermediaries of the transaction are commercial banks, and there are no guarantees.
- 2. Futures feature pricing, based on the movement of currency exchange rates, the intermediary is an exchange, and guarantees are the reserve deposit.
- Options and currency swaps.
Currency transactions can be performed both on the exchange and on the over-the-counter market (Forex Interbank Market, Forex).
2. Credit market
This market suggests a redistribution of spare funds from those who have them to those who do not have them. Unlike the investment market, the credit market is more complex (it has a three-tier structure) and has tighter requirements for participants to fulfill their obligations.
Credit market Levels:
The central bank and commercial banks. Here, the central bank acts as a regulator. Using loans, the central bank regulates the money supply, supports banks, facing temporary troubles, keeps the liquidity of the banking system, and covers the cash gaps.
Commercial banks and their clients
Credit relations between legal entities
3. Insurance market
It is a separate segment, as insurance companies are one of the main investors at the global level. Providing various kinds of insurance services, they accumulate capital, which they can temporarily invest in deposits, metals, and the stock market.
4. Investment market
It is a system based on free competition and partnerships between agents of investment activity. It has much in common with the stock market, where the funds are invested in securities, but it can also take the form of capital investments, fixed assets, etc. Simply put, the investment market provides investing money in any asset for subsequent earnings over some time due to an increase in an asset price or dividend payments.
5. Stock market: securities
It suggests a complex interaction between the market participants in terms of issuance and turnover of securities. Securities can be traded on both stock exchanges and beyond them. On the exchanges, you can trade only enlisted assets, i.e. which meet certain requirements. Assets can be:
Stocks. They can be common stocks and preferred stocks. Holders of common stock typically have voting privileges, whereas holders of preferred stock may not. However, preferred stockholders receive a fixed dividend from the company, while common shareholders may or may not receive one, depending on the decisions of the board of directors.
Bonds. Bonds can be (issuer – company), municipal (issuer – local authorities), state, or international (for example, Eurobonds). Bonds can also be preferential (the holder will be among the first to receive money during the liquidation of the company) and subordinated (more profitable, but riskier). There is a gradation in the coupon rate and yield to maturity.
Indices – consolidated instruments consisting of a basket of securities, which reflect average price statistics for the sector or for the industry in general.
Derivatives. They are derived instruments, which make up a multi-level system of securities.
ETF securities. An ETF is an index fund whose shares (units) are traded on an exchange. The fund’s investment structure can be anyone, ranging from securities of companies in a particular sector to a diversified portfolio, including stocks, gold, etc. Unlike shares of investment funds, you can perform any operations with ETF shares, as well as with securities.
As you see, the currency market only accounts for one-fifth of the financial market.
There is another, more general, but more exact classification of the world market: the currency market, the stock market, and the commodity market. The first one includes all operations with any currency (including cryptocurrency), the second one includes everything related to securities, and the third one provides trading metals, oil, goods, and services, including non-conventional investments (antiques, art, etc.). All three markets are connected by credit, investment, and other relationships.
The Forex market often combines different financial markets. For example, you can trade various CFDs, such as metals, oil, shares, and stock indexes at LiteFinance, thus starting your career in the financial markets.
Functions of the financial market
The financial market plays an important role in our modern civilized society. It aims to mobilize capital, distribute it between industries, control and maintain the reproduction process, and improve the efficiency of the economic system in general. The main functions of the financial market, carried out by its participants are the following:
Facilitate efficient relationships between all market participants, ranging from private individuals and individual investors to large institutional investors.
Supervise and regulate the processes held in the financial system: regulation of the money supply, compliance control for established rules by market participants, licensing, and development of legal provisions.
Mobilize the capital and allocate it so that it is used most efficiently and generates added value
Minimize risks, including fraud prevention (anti-money laundering). Ensure transparent pricing and avoid price manipulation.
Provide market liquidity
Ensure privacy and transparency of the transactions made
Provide necessary information
The activities of the financial market are based on national banks’ liabilities to control currency rates and set interest rates. Stock and currency markets, as well as commercial banks, are directly connected with the development of the financial assets market. The securities market is the most interesting segment of the financial market in terms of investment profitability.
Participants in the financial market
Each of us is a financial market participant in a way. Each of us works somewhere, making our contribution to the GDP rate, buys something, so indirectly affects the inflation rate and the level of consumer prices. Someone becomes an investor, buying a foreign currency or collectible coins, or investing in bank deposits, investment companies, using loans.
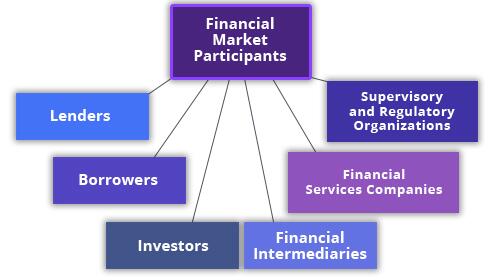
But still, economic science classifies the participants of the financial market, based on its segment. It suggests that the financial market, in a simplified form, is a relationship between two categories of participants: sellers and buyers. The third category includes intermediaries who are directly involved in transactions, providing assistance, facilitation, and guarantees. The same agent of the financial market can act simultaneously as the seller, the buyer, and the intermediary.
1. Currency market:
Sellers. The major sellers are the state and banks. The state that sells a currency through authorized bodies performs a regulatory function in this way. Sellers are also companies engaged in foreign economic activity (selling foreign currency earnings) and individuals.
Buyers. All agents, being sellers, can act as buyers.
Intermediaries. This category may include commercial
2. Credit market:
Borrowers. At the international level, borrowers are states and the ratio of external debt to GDP is considered one of the key statistical indicators of the state of the country’s economy. At the country level, borrowers are individuals and companies, local governments, etc. A good example of a multi-level structure of the credit market is the US mortgage system, where banks issued securities for mortgages to accumulate new capital for subsequent lending.
Lenders. These market participants possess spare capital and wish to increase it: individuals, investing their funds in deposits that will be subsequently directed to lending, and buyers of debt securities (insurance, pension, investment funds). In a way, any investor can be called a lender, since he/she gives spare money to gain interest rates and invest the income in development. The state can be also referred to as a lender, which creates liquidity and distributes the money to borrowers through the central bank.
Intermediaries. They are all who participate organization of the money distribution: banks, brokers, dealers, and managing investment companies. Insurance and pension funds can be also attributed to intermediaries, accumulating and distributing capital.
The credit market is closely related to investment and stock markets. For example, corporate bonds are both a tool for raising money and security at the same time. Government bonds are one of the favorite investment options with the lowest risk for investment funds.
3. Insurance market:
Insurers. These are companies, appropriately licensed to provide insurance services. There are insurance companies of open type (provide services to all market participants), captive insurers (being wholly owned and controlled by its insureds), and reinsurance risk management companies.
Insureds. Individuals, companies, and institutions buy insurance services to minimize the risks.
Intermediaries. There are no intermediaries, transactions are carried out directly between the insurer and the insured.
All markets are closely intertwined. As it has been mentioned above, insurance companies are also participants in the investment market. It also includes insurance instruments (for example, various swaps) used by agents of the stock market as well.
4. Investment market. Everyone, who invests money in a particular asset, is an investor. The intermediaries can be banks, exchanges, different kinds of funds, and so on.
5. Stock market:
Securities issuers. These include companies and organizations that issue certain securities: stocks, bonds, etc. When issuing, issuers agree that they must fulfill all the requirements specified (agreed) at the time of issue.
Investors. They are all those who buy securities to generate income. There are strategic (buying a majority stake) and minority (making up a portfolio, buying the securities to only generate income).
Intermediaries. Stock exchanges, banks, underwriters, ranking agencies, auditors, and other participants, engaged in facilitation for issuance and placement of securities.
The classification, described above, can be grouped in the following way:
The state and the central banks (regulating and supervising organizations). Managing the biggest volume of the capital, these agents mostly perform supervising and regulation functions.
Regulators (regulatory and supervisory institutions). Establishments that don’t take a direct part in transactions (that is why they can’t be referred to as intermediaries), but perform a controlling function. The supervisory function is also carried out by the central bank and the state government, but it can also be a separate institution, like a self-regulatory organization (SRO).
Financial Services Companies (organizations providing financial market services and financial intermediaries). These are institutions involved in organizational work: currency, stock and commodity exchanges, brokers, underwriters, auditors, depositories, registrars, and clearing and consulting companies.
Banks (financial intermediaries). They are intermediaries involved in capital distribution, market regulation, and supervision for established rules compliance.
Legal entities (lenders, investors, borrowers). The most extensive group of participants: companies engaged in the placement of clients’ pension savings, investment services, insurance companies, hedge funds, trust management companies, brokers, dealers, individual lending organizations, companies engaged in any type of financial activity, participating in money turnover.
Individuals (lenders, borrowers, investors): traders, speculators, individual asset managers, long-term investors, and just ordinary people, as it was mentioned at the beginning of the part.]
Important indicators of the financial market – a note for trader
For efficient trading and a perfect grasp of Forex affairs, a trader needs to know the indicators that help assess the situation in the financial market. These indicators include periodic releases of macro- and microeconomic data on the market state intended for more accurate forecasts and productive analysis. GDP, unemployment and inflation levels, currency or securities growth or fall rates also belong to those indicators. As a rule, experienced traders actively use economic calendars freely provided by brokers. I recommend you take up this habit if you haven’t yet. There is a brief description of some most important indicators, recorded in the economic calendar, and some tips on how to analyze them:
Interest rate. It is one of the major economic tools to manage the money supply, thereby adjusting inflation. The interest rate gives loans to commercial banks. A higher interest rate increases interest rates for credits and deposits and encourages consumers to invest. This, in turn, reduces the inflation rate. The influence of raising the interest rate depends on a country’s economy. For advanced economies (for example, the USA), a higher interest rate increases the exchange rate of the national currency. In less developed countries, raising the interest rate can be seen as a try to curb stagnation and so increase investors’ interest.
Non-Farm Payrolls. Report on the change in the number of jobs in the US non-farm sector. It is considered to be one of the most news reports, but its impact on the US dollar rate lasts a relatively short time (a few hours). It is released on the first Friday of the month at 1.30 p.m. GMT. In theory, the US dollar exchange rate will be influenced if the Non-Farm actual data deviates by more than 40,000 from the forecasts. In practice, much depends on the accompanying statistics and investors’ sentiment.
Consumer Price Index (CPI). It measures changes in the price level of a market basket of consumer goods and services purchased by households in the country. Changes in the CPI are used to assess price changes associated with the cost of living The index for the current year is analyzed, and compared to the benchmark (reference) indicator. The statistical base for calculation is recommended by the IMF, EBRD, and UN, but there is no single approach, each country has its peculiarities of calculation. The calculation methodology can be based on the Lowe index, Paasche, and Laspeyres price indices. If the index declines it means that consumer purchasing power (real demand) also declines and can partially suggest a higher inflation growth rate.
I think everything is clear about such indicators as GDP, inflation, and unemployment: the better the indicator, the more positive the sentiment of investors in the currency and stock markets.
An important point: the economic calendar is only an information complementary tool and it can in no way serve as the major tool to base trading strategies on. At the time of the news release, the market is especially volatile; therefore, the calendar is often used the other way around to exit trades.
If you are still willing to try trading on economic news, I offer you a few tips:
Compare the actual value with the forecast. If, for example, the GDP growth was 2%, compared to the forecast of 2.5%, it would have a negative influence on the market. Keep in mind, that the data can be revised.
Assess the chances for an event and investors’ expectations. For example, if the Fed is expected to hike the federal funds rate at the upcoming meeting, investors will consider it in advance and there won’t be any strong swings at the moment of the news release.
Compare the news importance with other factors. For example, while in quiet times, the release of statistics on the US crude oil stockpile had a quite strong influence on the foreign exchange rates, as well as other trading instruments, then, during the peak of the US-China trade war, these data were hardly noticed.
To try trading in the financial markets, register and begin your career as a successful trader.
That’s all for now.
Let’s discuss the article in the comments together.
See you later, friends!
P.S. Did you like my article? Share it on social networks: it will be the best “thank you” 🙂
Ask me questions and comment below. I’ll be glad to answer your questions and give the necessary explanations.
Useful links:
I recommend trying to trade with a reliable broker here. The system allows you to trade by yourself or copy successful traders from all across the globe.
Use my promo code BLOG to get a deposit bonus of 50% on the LiteFinance platform. Just enter this code in the appropriate field while depositing your trading account.
Telegram chat for traders: https://t.me/litefinancebrokerchat. We are sharing the signals and trading experience
Telegram channel with high-quality analytics, Forex reviews, training articles, and other useful things for traders https://t.me/liteforex